1998: Google Is Born
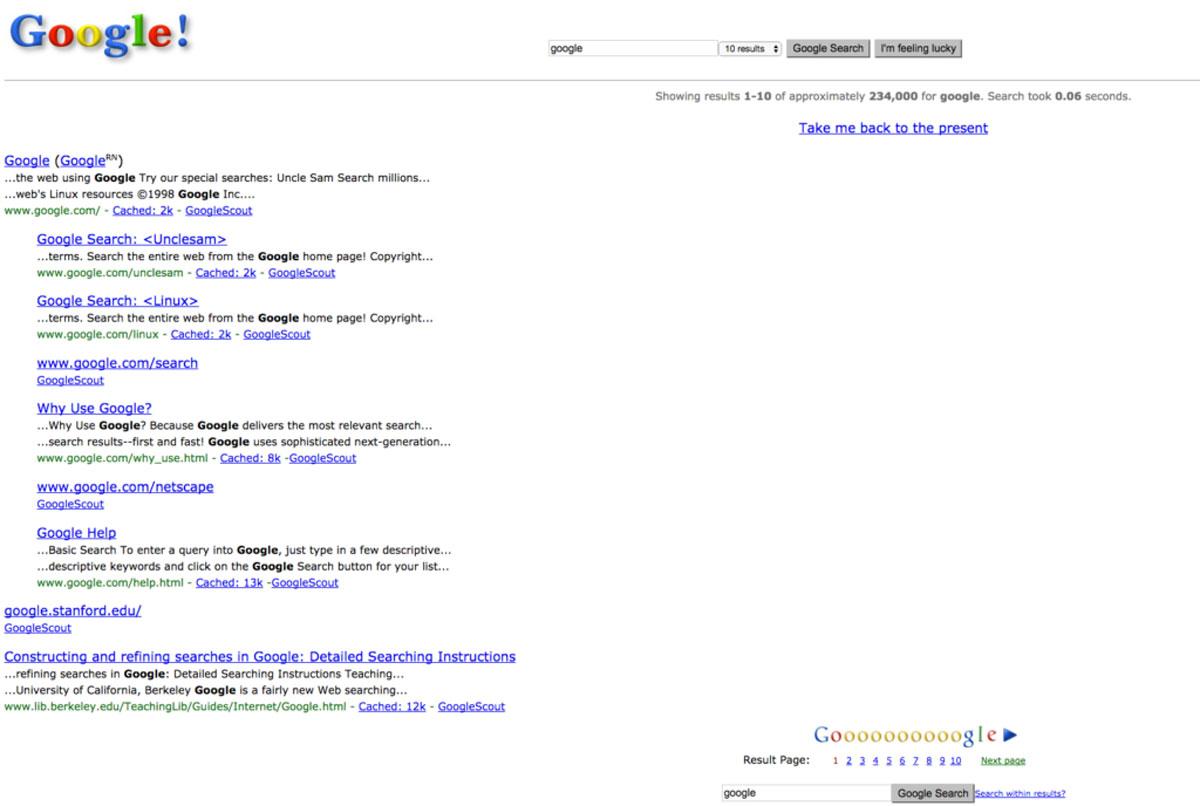
Google’s inception actually dates back to 1995 at Stanford University. Two students, Larry Page and Sergey Brin, developed a dorm room search engine project that eventually sparked the interest of Silicon Valley investors. In August 1998, Google Inc. was born.
1998 Google was Google in beta, so it was still well on its way to becoming the best search engine. Think minimalist chic Google. Google ads and local listings weren’t a thing yet, so Google’s SERP featured a lot of white space. But that all started to change after the turn of the century.
1999 & 2004: Google’s Terrible Twos & Toddler Years
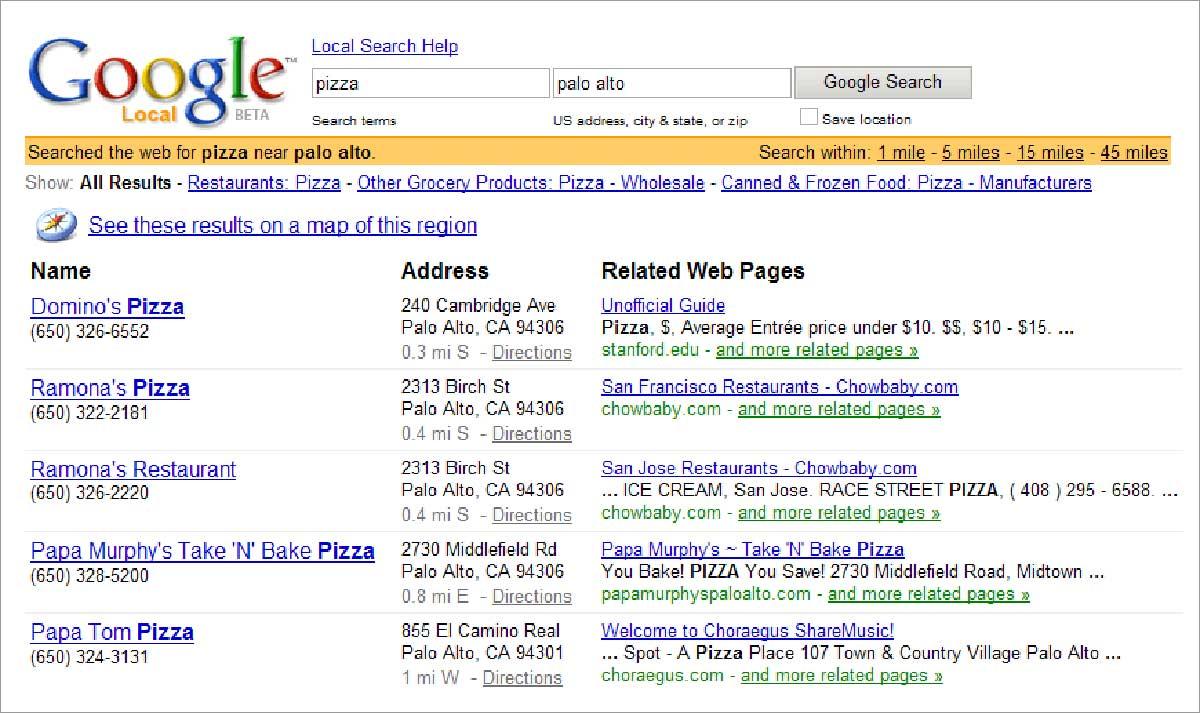
Google started to change between 2003 and 2004. The introduction of online local listings, All Results, and Google Ads were the biggest Google algorithm updates in the company’s early years.
Google introduced online local listings to help users find results tied to their specific area. The All Results tab allowed users to search a variety of search options, and Google Ads… well, they continue to frustrate the masses.
Google Ads served as a reminder that Google is a business at the end of the day. A business that made $162.45 billion from search ads in 2022, making search ads the company’s top revenue source to date.
Google also started cracking down on spammy search results before other search engines. The company worked hard to ensure their results were the most accurate and less likely to cause users headaches and frustration.
Google Algorithm Updates from 2005-2010
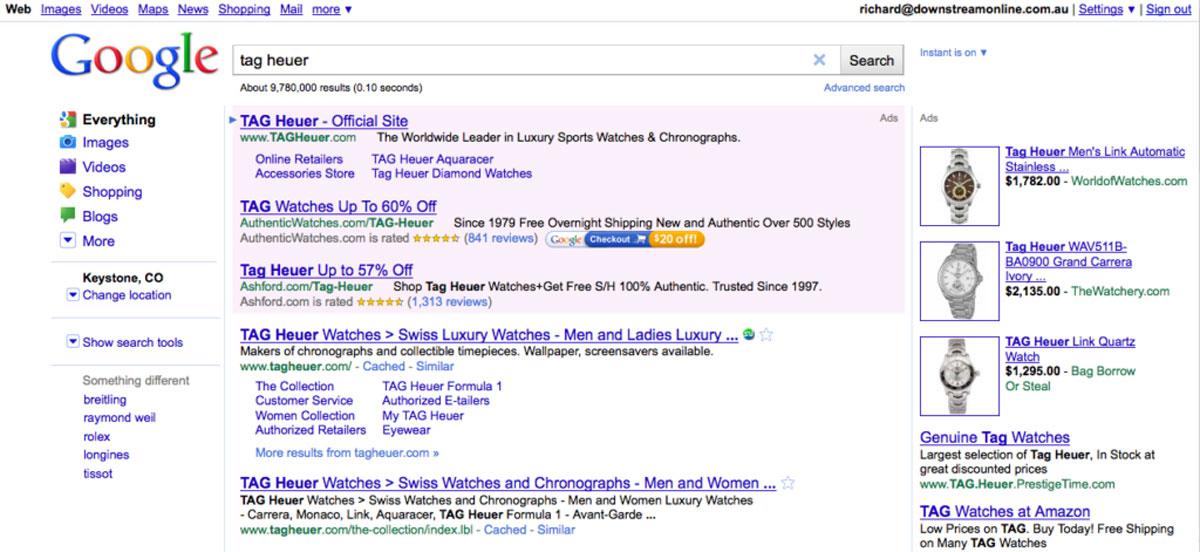
“Minimalist chic” Google disappeared after the advent of Google Ads, and Google’s SERP now began to feel a bit more cluttered.
On the bright side, Google Suggest arrived in 2007 allowing users to shave seconds off of their search time, and giving us all hilarious insight into the searches of our peers.
Google got rid of their Feeling Lucky button that let users bypass those exhausting ads and go straight to the website of the first search result.
The button still exists today, but around the 2009-2010 mark, with the combination of Google Instant (also gone) and Google Suggest, the button was basically defunct.
Advanced Search was still part of the regular search function in 2010 and other search tools appeared on the left-hand side of the SERP, allowing users to tap into a more specific search query.
Unlike today’s results, the SERP design was much more vertical; notice how the sitelinks under the primary domain are vertically aligned rather than today’s horizontally aligned sitelinks.
While this change may seem self-explanatory, a more horizontal approach means a) more search results per page and b) more detailed search results. These purely user-driven decisions were what led to major Google search updates. Next up: Google’s animal era.
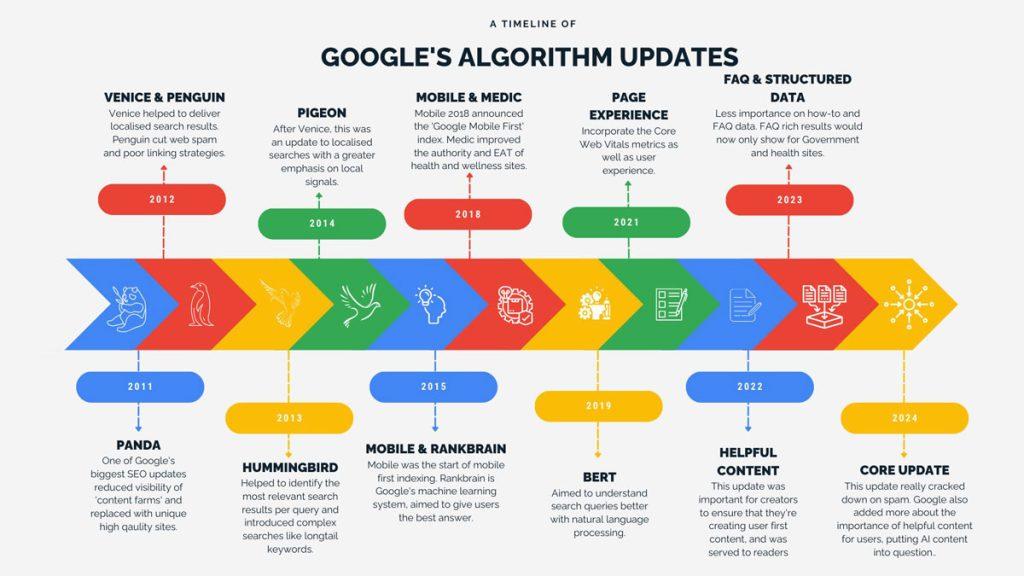
2011-2014: Pandas, Penguins, & Hummingbirds – OMG!
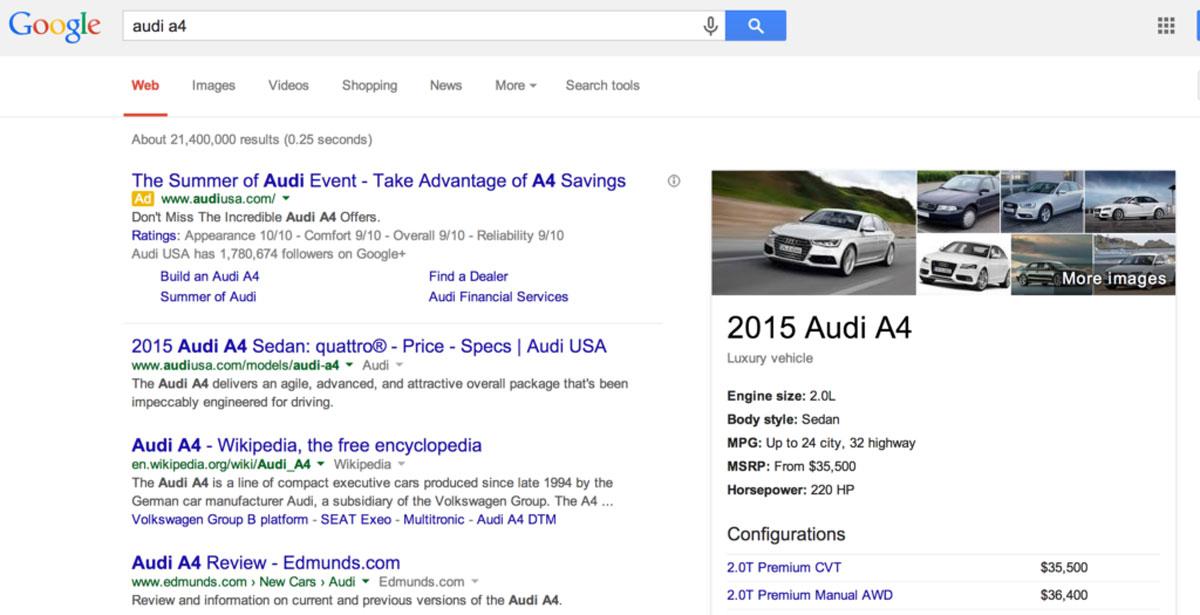
Pandas, penguins, and hummingbirds ruled this epoch of Google history. Let’s break down these updates in more detail.
2011: Google’s Panda Update
This update sought to “reduce rankings for low-quality sites—sites which are low-value add for users, copy content from other websites or sites that are just not very useful.”
The update, named after Navneet Panda (an inventor on the accompanying patent for the update, not a panda bear), launched in February 2011 and noticeably impacted rankings on 11.8% of queries.
2012: Google’s Penguin Update
Google’s Penguin update was a landmark update and one of the most notable SERP changes by Google. It cracked down on sites engaging in webspam tactics like keyword stuffing (unnaturally forcing keywords into content) and link spam (link inclusion purely to boost SEO).
Effectively, any site attempting to manipulate search rankings by abusing SEO tactics was punished by Google’s Penguin update. Google announced the update in 2012 and made it part of its core algorithm in 2016.
2013: Google’s Hummingbird Update
Aptly named for being “quick and precise,” Google’s Hummingbird update was essentially a rewrite of Google’s core algorithm.
The update improved Google’s ability to handle natural conversation in search queries. Instead of matching all words in a query to the words on a web page, Google began intuitively ignoring certain words that weren’t super relevant to a searcher’s meaning.
2013: The Knowledge Graph
Not an animal update, but still fun! Google launched the knowledge graph and corresponding Carousel in 2013 to create Universal Search. With this new feature, Google tossed all search results together instead of separating them out (video on top of an image on top of a domain).
Ads were limited to 3-4 above the foldwith more at the bottom of the page. Local listings were a part of the natural landscape of the search results (although fewer were shown). All Results were placed at the top of the results pages, and then visuals busted onto the scene.
Humans are visual creatures. Seeing an image with text helps us make connections to what we are seeing and searching for. By creating a more visual experience, users had an easier time finding what they needed through Search.
2014: Google Goes Mobile
By 2014, Google had successfully become our third, digital arm. We were using Google not only to search but to create ads, email, track our web analytics, and search for crawl errors.
Naturally, the SERPs were a reflection of each individual’s personal connection with the tech giant. Results were more personalized based on search history and the search tool became an extension of your results page.
But what was one of the most important transitions of 2014? Mobile.
Not only did Google start stressing the importance of a mobile-friendly site (followed by the highly anticipated Mobilegeddon in 2015), the aesthetic of their entire page changed between 2010 and 2014 to reflect a cleaner surface, fit for tinier screens.
And let’s not forget Voice Search. As a growing number of users adopted smartphones and began searching through mobile, the ability to quickly ask a question hands-free became more and more of a necessity. This was the dawn of the phrase “OK, Google.”
Google Algorithm Updates from 2015-2019
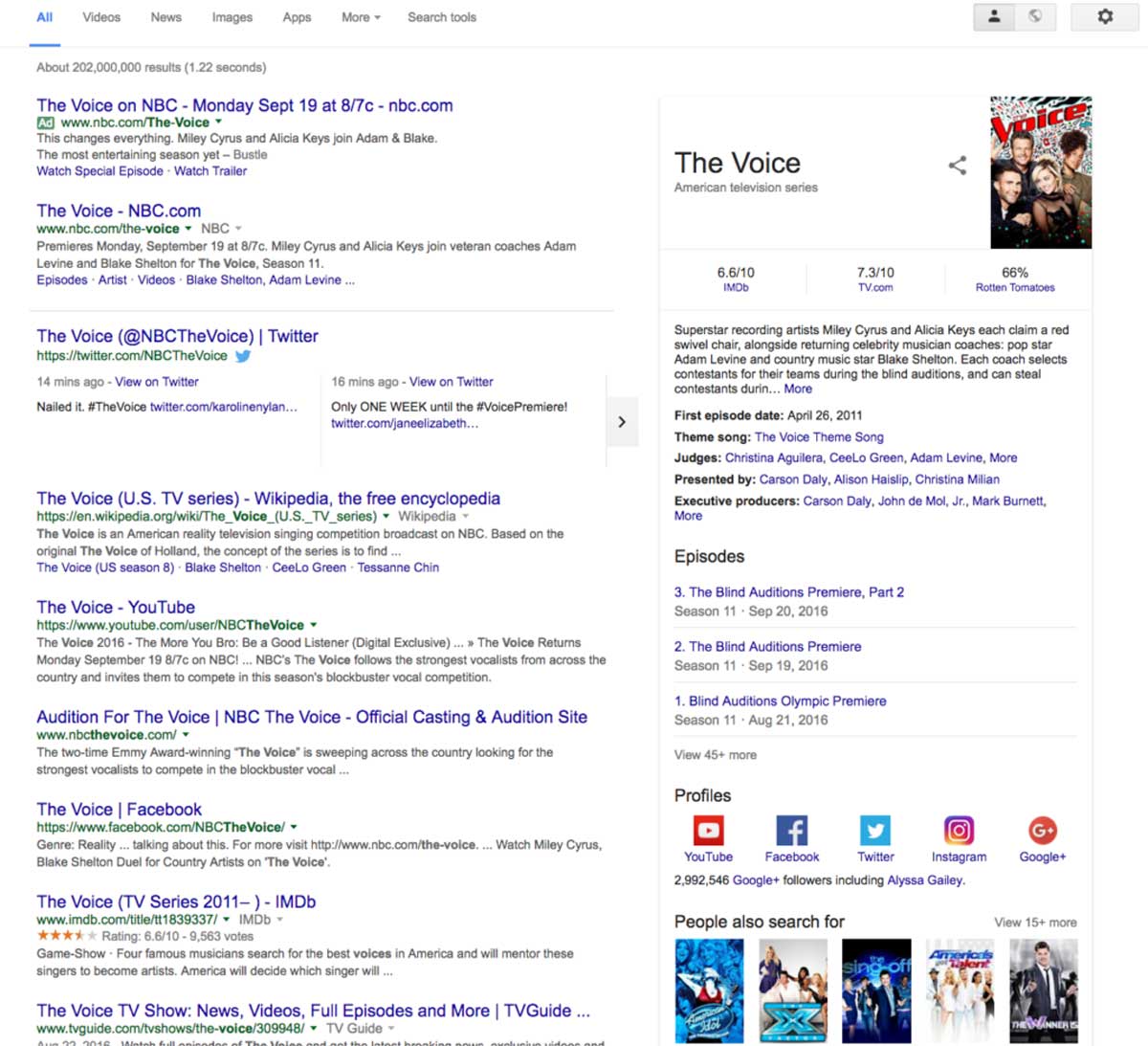
2015’s Mobilegeddon, or Mobile-Friendly Update, rewarded mobile-friendly websites with better SERP rankings. As we said, mobile became a massive game-changer for Google during this era.
The RankBrain update also arrived in 2015 and improved Google’s ability to understand new, complex queries. It was essentially Google’s first AI system and deep learning model, allowing Google to intuitively identify related words and concepts.
With new Answer Boxes to recent Tweets (now X’s?) and stories, there was often no reason to leave Google’s SERP page. Product Graphs also arrived at around this time, giving users a breakdown of a product before even visiting the site.
Images and videos appeared above the fold now. The “snack pack” version of local listings gave a user everything they needed to know about contacting a business before even clicking on its website link. And even with longer meta titles & descriptions, organic results got pushed further down the page.
In 2018, the Google Medic Update targeted medical sites that didn’t comply with Google’s E-A-T (now with an extra “E”) guidelines. Essentially, the update punished sites that were making unsubstantiated medical claims.
Google’s BERT Update in 2019 introduced a natural language processing (NLP) algorithm that helped Google understand the nuances of users’ search queries. BERT stood for Bidirectional Encoder Representations from Transformers. What’s that exactly?
Basically, BERT assesses all words in a complex search query to give users the most relevant results to their query, rather than just searching for content based on individual words. With the BERT update, the 2010s chapter of Google closed with some impressive new features.
So what’s happening with Google’s latest updates?
Google Algorithm Updates from 2020-2023
Google algorithm updates in recent years have mostly revolved around spam and product review updates.
Google cracked down on spammy links in 2022 by making improvements to SpamBrain, Google’s AI spam-detection system. Any sites engaging in spammy practices or violating Google’s spam guidelines saw worse SERP rankings.
For product review updates, Google began rewarding sites with rich, in-depth reviews rather than thin, low-quality reviews that weren’t as helpful to readers.
These product review updates coincided with Google’s Helpful Content Update. Essentially, the updates ensured users saw more helpful, high-quality, and original content.
Closing Thoughts After a Scroll Down Memory Lane
Google is constantly changing, and it’s safe to say Google will keep growing and changing for years to come. With ever-evolving AI technology and tools like Bard, search will become even easier.
In February 2023, Google announced, “Soon, you’ll see AI-powered features in Search that distill complex information and multiple perspectives into easy-to-digest formats, so you can quickly understand the big picture and learn more from the web.” With that said, having to balance UX with revenue-driving tools can be difficult. And staying on top of the latest Google search results trends and major Google search updates can be equally challenging.
In November 2023 Google announced a core algorithm update, which began on November 2 and was completed on November 28. To learn more about core updates, see the Google Search Central Blog.





















Comments